Chapter 3: Human Reproduction Class 12 Biology NCERT Solutions
Understand the human reproductive system, gametogenesis, and embryonic development with Chapter 3 NCERT Solutions. Download free PDFs for quick revision. Scroll down for detailed solutions that simplify difficult topics easily.
To Help You Excel: NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 – Human Reproduction
Our expertly written NCERT Solutions for Chapter 3 cover all Intext and Exercise questions in a clear, concise, and easy-to-understand format. With detailed diagrams, stepwise answers, and important facts highlighted, these solutions ensure that you grasp each topic thoroughly and are well-prepared for both exams and entrance tests.
What You Will Learn in Chapter 3 – Human Reproduction
This chapter introduces you to the human reproductive system, the processes involved in the formation of gametes, and the journey from fertilisation to the birth of a baby.
Key Topics Covered:
1. The Male and Female Reproductive Systems
– Structure and function of male and female reproductive organs
– Accessory glands and reproductive ducts
– Internal and external genitalia
2. Gametogenesis
– Spermatogenesis and oogenesis
– Hormonal regulation of gamete formation
– Differences in male and female gamete development
3. Menstrual Cycle
– Phases: Menstrual, follicular, ovulatory, and luteal
– Hormonal control involving FSH, LH, estrogen, and progesterone
– Biological significance and fertility window
4. Fertilisation and Implantation
– Ovulation, fertilisation in the fallopian tube
– Zygote and blastocyst formation
– Implantation in the uterus lining
5. Pregnancy and Embryonic Development
– Placenta formation and its functions
– Role of hormones like hCG, hPL, and oxytocin
– Parturition and lactation
Why Use Our NCERT Solutions for Chapter 3?
Each answer is prepared to help students understand difficult topics like gametogenesis, hormonal control, and embryonic development in a simplified and structured way. Our NCERT-based solutions are perfect for CBSE board exams and essential for NEET aspirants.
Highlights of Our Solutions:
– Comprehensive answers to all Intext and Exercise questions
– Accurate, labeled diagrams (male/female reproductive systems, gametes, etc.)
– Clear explanations of biological processes
– Real-world analogies to help with concept retention
– Important keywords and definitions highlighted
NCERT Solutions for Chapter 3 – Human Reproduction
Intext Questions:
– Well-explained answers to concept-checking questions
– Detailed structures of reproductive organs
– Gamete formation with hormonal involvement
Exercise Questions (Q.1 to Q.13):
– Thorough answers on menstrual cycle, spermatogenesis, fertilisation
– Explanation of parturition, lactation, and hormonal changes
– Diagrams of sperm, ovum, zygote development, and embryo
Download Chapter 3 Solutions PDF – Human Reproduction
Get complete offline access to solved NCERT questions with our free, printable PDF. Perfect for last-minute revisions and NEET prep.
What’s Inside the PDF:
– Well-organized solutions for Intext and Exercise questions
– High-quality diagrams and flowcharts
– Concise yet informative answers aligned with NCERT
Recommended Preparation Tips:
– Draw and label male and female reproductive systems from memory
– Understand hormonal control in gametogenesis and menstrual cycle
– Revise key events of fertilisation and implantation step-by-step
– Memorize the roles of hCG, oxytocin, relaxin, and prolactin
– Use flowcharts to trace zygote to embryo to fetus development
Additional Study Resources:
– Class 12 Biology Notes – Chapter 3
– NCERT Exemplar Solutions – Human Reproduction
– Important NEET-based MCQs from previous years
– Flashcards for hormones, stages, and reproductive structures
– Summary tables for menstrual phases and embryonic stages
Mastering Human Reproduction Starts Here
This chapter connects theoretical biology with real-life human physiology. With our detailed NCERT solutions, illustrations, and summaries, you’ll understand each step of human reproduction clearly and confidently. Build your foundation in Biology and score higher in both board exams and NEET!
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology – Chapter 3: Human Reproduction
Textbook Exercise Questions Answered
1. Fill in the blanks:
- (a) Humans reproduce sexually.
- (b) Humans are viviparous.
- (c) Fertilisation is internal in humans.
- (d) Male gamete is sperm and female gamete is ovum.
- (e) Zygote is diploid.
- (f) The process of release of ovum from a mature follicle is called ovulation.
- (g) Ovulation is induced by a hormone called Luteinising hormone (LH).
- (h) The fusion of male and female gametes is called fertilisation.
- (i) Fertilisation takes place in the fallopian tube (ampullary-isthmic junction).
- (j) Zygote divides to form blastocyst, which is implanted in uterus.
- (k) The structure which provides vascular connection between fetus and uterus is called placenta.
2. Draw a labelled diagram of male reproductive system
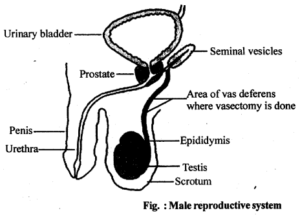
3. Draw a labelled diagram of female reproductive system
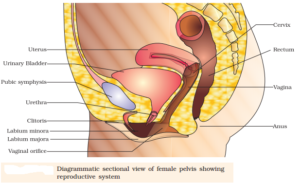
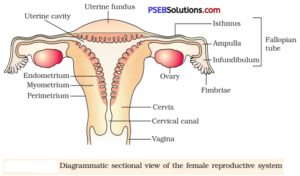

4. Write two major functions each of testis and ovary
Testis:
- Production of spermatozoa (sperms) via spermatogenesis.
- Secretion of testosterone, the male sex hormone.
Ovary:
- Production of ova (female gametes) via oogenesis.
- Secretion of estrogen and progesterone, the female sex hormones.
5. Describe the structure of a seminiferous tubule
Each seminiferous tubule is a highly coiled structure inside the testes. It is lined with:
- Spermatogenic cells (spermatogonia, primary and secondary spermatocytes, spermatids, and spermatozoa)
- Sertoli cells: Provide nourishment and structural support
- Surrounding the tubules are interstitial (Leydig) cells, which secrete testosterone.
6. What is spermatogenesis? Briefly describe the process of spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process of formation of sperm cells from spermatogonia in the testes.
Steps:
- Multiplication phase: Spermatogonia (2n) undergo mitosis.
- Growth phase: Some spermatogonia enlarge to become primary spermatocytes (2n).
- Maturation phase:
- Primary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis I → two secondary spermatocytes (n)
- Each secondary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis II → two spermatids (n)
- Spermatids mature into spermatozoa by spermiogenesis.
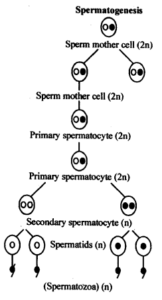
7. Name the hormones involved in regulation of spermatogenesis
- GnRH (Gonadotropin-releasing hormone): Stimulates release of LH and FSH.
- FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone): Stimulates Sertoli cells.
- LH (Luteinising Hormone): Stimulates Leydig cells to produce testosterone.
- Testosterone: Promotes spermatogenesis.
8. Define spermiogenesis and spermiation
- Spermiogenesis: Transformation of spermatids into mature spermatozoa.
- Spermiation: Release of mature sperms from Sertoli cells into the lumen of seminiferous tubules.
9. Draw a labelled diagram of sperm
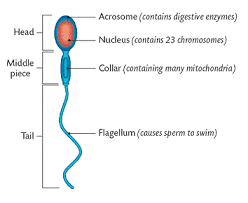

10. What are the major components of seminal plasma?
- Seminal plasma is rich in:
- Fructose (energy source)
- Calcium ions
- Enzymes and prostaglandins
- It is secreted by the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands, and it helps in sperm motility and survival.
11. What are the major functions of male accessory ducts and glands?
- Accessory Ducts (e.g., epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory duct): Transport, store, and mature sperm.
- Accessory Glands:
- Semen vesicles: Add fructose and prostaglandins
- Prostate gland: Adds fluid for sperm motility
- Bulbourethral glands: Lubrication and neutralisation of urine residues
12. What is oogenesis? Give a brief account of oogenesis
Oogenesis is the formation of ova (eggs) in the ovary.
Stages:
- Multiplication phase: Oogonia (2n) divide mitotically during fetal life.
- Growth phase: Oogonia enlarge to form primary oocytes (2n), which enter meiosis I but arrest at prophase I.
- Maturation phase (at puberty):
- Primary oocyte completes meiosis I → one secondary oocyte (n) + one first polar body
- Meiosis II starts but pauses at metaphase until fertilisation
- On fertilisation: Meiosis II completes → Ovum (n) + second polar body
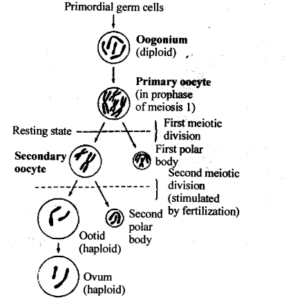
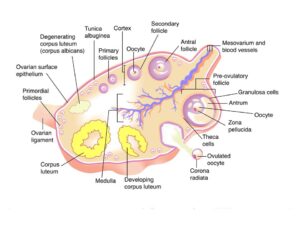
13. Draw a labelled diagram of a section through ovary

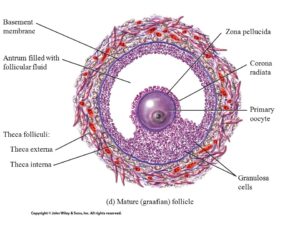
14. Draw a labelled diagram of a mature Graafian follicle

15. Name the functions of the following:
- Fimbriae: Help in capturing the ovum after ovulation.
- Infundibulum: Funnel-shaped region of fallopian tube; guides ovum.
- Isthmus: Narrow region that connects fallopian tube to uterus.
- Ampulla: Site of fertilisation.
- Endometrium: Innermost layer of uterus; supports implantation.
- Myometrium: Muscular middle layer; helps in childbirth contractions.
- Acrosome: Cap-like structure in sperm; contains enzymes to penetrate ovum.
- Sperm tail: Provides motility to sperm.
16. Identify True or False statements:
- (a) Fertilisation is possible if ovum and sperms are transported simultaneously to ampullary region. → True
- (b) Implantation occurs in fallopian tube. → False (Occurs in uterus)
- (c) Only one sperm fertilises the ovum. → True
- (d) Corpus luteum secretes estrogen. → False (Secretes progesterone)
- (e) Oogenesis starts before birth in females. → True
17. What is menstrual cycle? Which hormones regulate it?
The menstrual cycle is a 28-day cyclic event in females involving preparation for fertilisation and shedding of uterine lining in the absence of pregnancy.
Regulated by:
- FSH & LH from anterior pituitary
- Estrogen and Progesterone from ovaries
18. What is parturition? Which hormones are involved?
Parturition is the process of childbirth, triggered by:
- Oxytocin: Causes uterine contractions
- Relaxin: Relaxes pelvic ligaments
- Positive feedback between uterine contractions and oxytocin release initiates labour.
19. What is the role of oxytocin in parturition?
- Stimulates strong uterine contractions
- Promotes expulsion of fetus from uterus
- Involved in positive feedback mechanism to increase contraction strength
20. What is lactation? Name the hormone responsible for milk production
Lactation is the process of milk secretion from mammary glands post-childbirth.
- Hormone: Prolactin (stimulates milk production)
- Oxytocin helps in milk ejection (let-down reflex)