Chapter 14: Ecosystem Class 12 Biology NCERT Solutions
Master the concepts of energy flow, ecological pyramids, and nutrient cycles with Chapter 14 NCERT Solutions. Download free PDFs for quick learning. Scroll down to access complete, organized answers.
What You Will Learn in Chapter 14 – Ecosystem
This chapter provides insights into the organization and functioning of ecosystems. It explains how energy flows through different trophic levels and how nutrients are cycled between biotic and abiotic components.
Key Topics Covered:
1. Ecosystem – Structure and Function
Definition of ecosystem and its components.
Biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) factors.
Structure: Producers, consumers (primary, secondary, tertiary), and decomposers.
Functions of an ecosystem: Energy flow, nutrient cycling, and ecological balance.
2. Productivity of an Ecosystem
Primary Productivity:
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) – Total energy captured by producers.
Net Primary Productivity (NPP) – Energy available to consumers after plant respiration.
Secondary Productivity: Energy transferred to herbivores and carnivores.
Factors affecting productivity: Light, temperature, water, nutrients.
3. Decomposition
Breakdown of complex organic matter by decomposers (bacteria and fungi).
Processes: Fragmentation, leaching, catabolism, humification, and mineralization.
Importance of decomposers in nutrient recycling.
4. Energy Flow in Ecosystems
Unidirectional flow of energy from the sun to producers and through trophic levels.
10% law of energy transfer between trophic levels.
Energy loss as heat at each level.
5. Food Chains and Food Webs
Food Chain: Linear sequence of energy transfer (e.g., grass → deer → tiger).
Food Web: Network of interconnected food chains showing complexity.
Types: Grazing food chain and detritus food chain.
6. Ecological Pyramids
Graphic representation of trophic levels.
Types of pyramids:
Pyramid of Number
Pyramid of Biomass
Pyramid of Energy (always upright)
Inverted and upright pyramids depending on ecosystem type.
7. Ecological Succession
Gradual and sequential changes in species composition in an area.
Types:
Primary succession – On newly formed habitats (e.g., lava, bare rocks).
Secondary succession – On existing ecosystems disturbed by events.
Seral stages leading to climax community.
8. Nutrient Cycling (Biogeochemical Cycles)
Movement of nutrients between living and non-living components.
Types of cycles:
Gaseous cycles (carbon, nitrogen)
Sedimentary cycles (phosphorus)
Role of decomposers and environment in recycling.
9. Ecosystem Services
Benefits ecosystems provide to humans and the environment.
Examples:
Climate regulation
Purification of air and water
Pollination of crops
Cycling of nutrients and soil formation
Estimated value of global ecosystem services.
Why Use Our NCERT Solutions for Chapter 14?
Our expertly crafted NCERT solutions for Chapter 14: Ecosystem offer a comprehensive and easy-to-understand explanation of key ecological concepts. These solutions help students build strong foundational knowledge for board exams and competitive exams like NEET.
Highlights of Our Solutions:
Concise, accurate answers to all NCERT Intext and Exercise questions.
Diagrams and flowcharts to explain energy flow, pyramids, and nutrient cycles.
Real-world examples of food chains, ecological succession, and productivity.
Definitions and explanations of critical terms like NPP, food web, seral stages, etc.
Ideal for revision and quick concept clarity.
NCERT Solutions for Chapter 14 – Ecosystem
Intext Questions:
Stepwise explanation of decomposition processes.
Diagrams of energy flow and trophic levels.
Detailed answers on productivity and energy loss across food chains.
Exercise Questions (Q.1 to Q.10):
Conceptual and application-based answers on ecological pyramids, succession, and ecosystem services.
Clear breakdown of differences between GPP and NPP, primary and secondary succession, food chain vs. food web.
Case-based questions on nutrient cycling and productivity.
Download Chapter 14 Solutions PDF – Ecosystem
Access a free, printable PDF with complete NCERT solutions to revise offline and boost exam performance.
What’s Inside:
Fully solved NCERT questions.
Diagrams of food chains, energy pyramids, and cycles.
Glossary of important ecological terms.
Recommended Preparation Tips:
Understand energy flow: Learn the unidirectional nature of energy and the 10% law.
Revise ecological pyramids: Know their types, shapes, and significance.
Study succession stages: Compare primary vs. secondary succession clearly.
Master nutrient cycles: Use diagrams to grasp the nitrogen and carbon cycles.
Use real-life examples: Relate concepts to natural ecosystems like forests, lakes, and grasslands.
Additional Study Resources:
Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Notes – Ecosystem (Quick revision format).
NCERT Exemplar Questions with Solutions for advanced practice.
NEET-based MCQs and practice papers.
Flashcards for ecosystem terms and definitions.
Flowcharts for ecological processes like succession and decomposition.
Mastering the Concept of Ecosystem
Chapter 14 builds a clear understanding of how ecosystems function, maintain balance, and support life. With this knowledge, students can appreciate the delicate links between organisms and their surroundings and the importance of conserving our natural resources.
Master this chapter to gain a deeper perspective on the biological and environmental processes shaping our planet.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem
1. Fill in the blanks.
(a) Plants are called as Autotrophs because they fix carbon dioxide.
(b) In an ecosystem dominated by trees, the pyramid (of numbers) is Spindle type.
(c) In aquatic ecosystems, the limiting factor for the productivity is Sunlight.
(d) Common detritivores in our ecosystem are Earthworm, bacteria & fungi of decay and vulture.
(e) The major reservoir of carbon on earth is Oceans.
2. Which one of the following has the largest population in a food chain?
Ans: (d) Decomposers
3. The second trophic level in a lake is–
Ans: (b) Zooplankton
4. Secondary producers are
Ans: (d) None of the above
5. What is the percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) in the incident solar radiation?
Ans: (b) 50%
6. Distinguish between:
- (a) Grazing food chain and detritus food chain:
Grazing food chain begins with producers and ends with top carnivores. It derives energy from the sun.
Detritus food chain starts with dead organic matter and depends on decomposers and detritivores. - (b) Production and decomposition:
Production is the synthesis of organic matter by autotrophs using sunlight.
Decomposition is the breakdown of complex organic matter into simpler inorganic substances. - (c) Upright and inverted pyramid:
An upright pyramid shows a decrease in biomass/number at higher levels (e.g., grassland),
whereas an inverted pyramid shows an increase (e.g., tree ecosystem). - (d) Food chain and food web:
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms involved in energy transfer,
whereas a food web is a network of interconnected food chains. - (e) Litter and detritus:
Litter is the organic matter fallen on the soil surface, while detritus is decaying matter below the surface. - (f) Primary and secondary productivity:
Primary productivity is the rate of energy fixation by producers.
Secondary productivity is the rate of biomass generation by consumers.
7. Describe the components of an ecosystem.
Abiotic components: Inorganic substances (minerals), organic matter, and climatic factors like temperature, pH, and sunlight.
Biotic components:
– Autotrophs (e.g., green plants, photosynthetic bacteria)
– Heterotrophs: Primary (herbivores), Secondary (carnivores), and Top consumers
– Decomposers: Microorganisms like bacteria, fungi, etc.
8. Define ecological pyramids and describe with examples, pyramids of number and biomass.
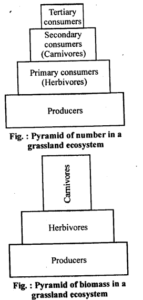
Ecological pyramids graphically represent the number, biomass, or energy at each trophic level.
Pyramid of number: Shows the number of organisms at each level (e.g., upright in grassland).
Pyramid of biomass: Represents biomass at each level. Upright in forests/grasslands; inverted in aquatic ecosystems.
9. What is primary productivity? Give a brief description of factors that affect primary productivity.
Primary productivity is the rate at which producers synthesize biomass using sunlight.
Factors affecting primary productivity:
– Plant species
– Sunlight
– Temperature
– Soil water
– Nutrient availability
10. Define decomposition and describe the processes and products of decomposition.
Decomposition is the breakdown of complex organic matter into simpler inorganic compounds by decomposers.
Processes: Fragmentation → Leaching → Catabolism → Humification → Mineralisation
Products: CO₂, water, humus, nutrients
11. Give an account of energy flow in an ecosystem.
Energy flow is unidirectional. Sunlight is captured by producers, transferred to herbivores, and then to carnivores.
Only 10% of energy is passed on to the next level (10% Law); rest is lost as heat or used in metabolic processes.
12. Write important features of a sedimentary cycle in an ecosystem.
Sedimentary cycles involve the circulation of nutrients like phosphorus and sulphur from soil/rocks.
Example: In the phosphorus cycle, phosphorus is taken up by plants, transferred to animals, and returned to soil via decomposition.
13. Outline salient features of carbon cycling in an ecosystem.
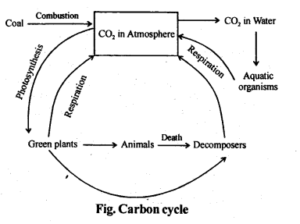
Carbon is exchanged between the atmosphere, organisms, and earth.
Plants fix atmospheric CO₂ via photosynthesis. Carbon passes through trophic levels and returns via respiration, decomposition, and burning of fossil fuels.